Wireless Solutions, Best Solutions For You !
Ads 468x60px
Popular Posts
-
The MU to MU disallow feature allows the RF Switch to block communications exchanged between clients associated to a WLAN.With the Motorola ...
-
Pre-Requisites: Requirements: The following requirements must be met prior to attempting this configuration: One (or more) RF Switc...
-
RADIUS Authentication Attributes: The RADIUS protocol follows client-server architecture and uses the User Datagram Protocol (UDP) as de...
-
LDAP Server can be used as the database with WS5100 radius server. This document provides the details of configuration need to done for WS5...
-
WS5100 login: cli User Access Verification Username: restore Password: restoreDefaultPassword WARNING:This will wipe out the con...
-
IPSec VPN offers the security and encryption features necessary to protect enterprise data, voice, and video traffic as it traverses public...
-
Components Used: The information in this document is based on the following hardware and software versions: · 1 x RFS4000 Swit...
-
The following section outlines the configuration steps required to configure 802.11i with 802.1X and pre-shared keys on a RF Switch: 1) ...
-
Snipe-IT is a free and open source, cross-platform, feature-rich IT asset management system built using a PHP framework called Laravel ...
Motorola_Wireless IDS
Overview:
Threats to WLANs are
numerous and are potentially devastating to business and day to day operations.Security
issues ranging from unauthorized Access Points (APs) or 802.11 attacks can
plague a WLANand provide risk to sensitive information as well as impact
performance.To aid in the detection and defense of potential threats, Motorola
offers enterprises with a layered approach to security that includes integrated
unauthorized AP detection, unauthorized AP containment and Wireless Intrusion
Detection.
Pre-Requisites
- The following requirements must be met prior to
attempting this configuration:
- One or more RF Switches are installed and operational
on the network.
- One or more AP300 Access Ports configured and adopted
by the RF Switch.
- A Windows XP workstation with a console, telnet or SSH
client is available to perform configuration on the RF Switches.
- One or more standalone Access Points to verify
unauthorized AP detection and containment.
- One or more wireless workstations are available to test
and verify unauthorized AP containment and intrusion detection.
- The reader has read the Motorola RFS Series Wireless
LAN Switches - WiNG System Reference Guide.
Components Used:
The information in this
document is based on the following Motorola hardware and software versions:
- 1 x RFS6000 Version 3.3.
- 5 x AP300s.
Registered users may
download the latest software and firmware from the Motorola Technical
Support Site
http://support.symbol.com.
Configuration:
The following sections
outline the configuration steps required to enable unauthorized AP detection
and intrusion detection on an RF Switch:
1) Unauthorized AP
Detection
2) Unauthorized AP
Containment
3) Mobile Unit
Intrusion Detection
4) SNMP Traps
Unauthorized AP
Detection:
As shown in figure 3.1,
an RF Switch is deployed at a site with four AP300s. The administrator wants to
enable unauthorized AP detection to be proactively alerted when any APs are
added or removed from the site.
To provide unauthorized
detection, three AP300s will be configured to perform single channel scanning while
providing WLAN services to users. The three APs will monitor the 2.4GHz
channels 1, 6 and 11 and 5GHz channels 36, 40 & 48. The fourth AP300 will
be configured as a dedicated detector AP and will monitor all channels within
the regulatory domain. Using three AP300s with single channel scanning and
a dedicated detector APs
will provide the RF Switch with complete visibility into the 2.4GHz and 5GH z spectrum
at this site.
Web UI Configuration
Example.
The following configuration
example will demonstrate how to globally enable unauthorized AP detection on
an RF Switch and configure AP300 scanning options using the Web UI:
1) In the menu
tree select Network > Access Port Radios then select the Configuration tab.
Highlight and select an AP300
radio then click Edit.
In the Network >
Access Port Radio > Configuration window under Properties, check the option Single-channel
scan for Unapproved APs or Dedicate this AP as a Detector AP. In this
example radios 1-4 & 7-8 will be configured for single channel
scanning and radios 5-6 will be configured as dedicated detectors.
In the menu tree select
Security > Access Point Detection then select the Configuration tab. Check
the Enable to globally enable unauthorized AP detection on the switch then
click Apply.
If Motorola devices are
being deployed, you may optionally enable MU Assisted Scanning which leverages
Motorola client extensions on Motorola devices to provide additional
detection.
In the menu tree select
Security > Access Point Detection then select the Unapproved APs (AP Reported)
tab. All detected APs will be listed in this table.
Click Save to apply and save changes
Mobile Unit Intrusion
Detection:
To provide proactive
protection against active intrusion attempts, mobile unit intrusion detection will
be enabled on the RF Switch. The RF Switch can detect numerous intrusion
violations and can alert administrators of intrusion attempts and attacks
as well as provide mitigation by automatically blacklisting mobile units
triggering the violation.
In this example the
following configuration will be performed:
1) The global
detection window will be increased from 10 seconds to 60 seconds.
2) The MU
Excessive Authentication Failure threshold will be set to 10. If 10
authentication failures occur from a specific MU within a 60 second
window, an alarm will be generated and the MU blacklisted.
3) The Radio and
Switch Excessive Authentication Failure thresholds will be set to 20. If
20 authentication failures occur on a single radio or globally on the RF
Switch the within a 60 second window, an alarm will be generated.
4) The Time to
Filter for the Excessive Authentication Failure intrusion violation will be set
to 300 seconds. If an MU triggers the intrusion violation, the MUs MAC
address will be filtered for 5 minutes.
Web UI Configuration
Example:
The following
configuration example will demonstrate how to enable mobile unit intrusion
detection for excessive authentication failures using the Web UI:
1) In the menu
tree select Security > Mobile Unit Intrusion Detection then select the
Configuration tab. In the Detection Window field specify the detection window
interval (in seconds) the RF Switch will use to scan for violations. In
this example a 60 second detection window will be configured. Click Apply.
In the Violation
Parameters table, locate Excessive Authentication failure then enter a
threshold value in the Mobile Unit, Radio and Switch fields. Additionally
in the Time to Filter field enter a value (in seconds) that the mobile
unit will be blacklisted when violations occur. In this example the Mobile
Unit threshold will be set to 10 and the Radio and Switch thresholds set to 20.
Additionally the Time to Filter violating MUs will be set to 300. Click
Apply
Select the Filtered MUs tab. Any mobile units that have violated an event will be listed in the table.
Click Save to apply and save changes.
SNMP Traps:
To provide proactive
alerting of unauthorized APs and intrusion events, an RFMS 3.0 server will
be defined on the RF Switch as an SNMP trap receiver and unauthorized AP
and intrusion detection traps enabled. When the RF Switch detects an unauthorized
AP or a intrusion detection violation, the RF Switch will forward an SNMP
trap to the RFMS server
Web UI Configuration
Example:
The following
configuration example will demonstrate how to enable SNMP traps to an RFMS 3.0
server for unauthorized APs and mobile unit intrusion detection violations
using the Web UI:
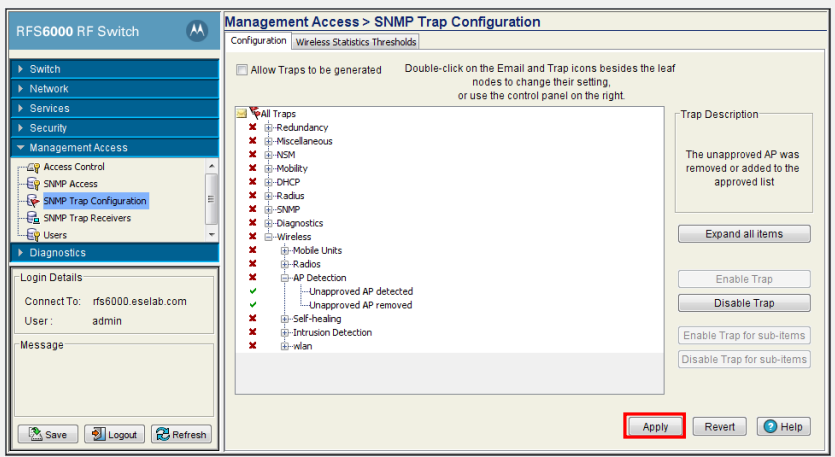
1) In the menu
tree select Management Access > SNMP Trap Receivers then click Add
In the Management Access > SNMP Traps window, enter the IP Address of the RFMS 3.0 server.
Under Protocol Options select the SNMP version then click OK.
In the menu tree
select Management Access > SNMP Trap Configuration then select theConfiguration
tab. In the All Traps tree, locate AP Detection then select the Unapproved AP detected
and Unapproved AP removed traps. Click Enable Trap
Click Apply.
In the menu tree select
Management Access > SNMP Trap Configuration then select the Configuration
tab. In the All Traps tree, locate Intrusion Detection then select the
Excessive violation from mobile unit, Excessive violation from radio and
Excessive violation from switch traps. Click Enable Trap.
Click Apply.
In the menu tree select
Management Access > SNMP Trap Configuration. Check the option Allow Traps to
be generated then click Apply
RF Switch Running Configuration:
The following shows the running configuration of the RFS6000 switch used to create this guide:
RFS6000# show running-config
Nhãn:
Motorola,
Wireless IDS
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)
Recent Posts
Blog Archive
-
▼
2014
(36)
-
▼
February
(36)
- WiNG How-To Guide Wireless Filters - Configuration
- WiNG How-To Guide Wireless Filters - Overview
- WiNG How-To Guide 3G WAN - Configuration
- WiNG How-To Guide 3G WAN
- WiNG How-To Guide 802.11i - Configuration
- WiNG How-To Guide 802.11i - Overview
- WiNG How-To Guide Digital Certificates - Configura...
- WiNG How-To Guide Digital Certificates - Overview
- WiNG How-To Guide Microsoft L2TP/IPSec VPN Client-...
- WiNG How-To Guide Microsoft L2TP/IPSec VPN Client-...
- WiNG How-To Guide MU to MU Disallow
- Network Address Translation-Configuration
- Network Address Translation - Overview
- WiNG How-To Guide Secure Beacons - Configuration
- WiNG_ How To Secure_Beacons - Overview
- L3 Mobility Implementation With WS5100 version 3.0
- WiNG RADIUS Attributes
- SMART-RF – Overview
- Mesh Networking
- MWAN 6300 Series - MOTOMESH Solo
- Motorola Mesh Portfolio - Overview
- WS5100 3.0 Radius & WPA Implementatio - Configuration
- WS5100 3.0 Radius & WPA Implementatio - Overview
- WiNG How-To Guide RSA SecurID_Configuration
- WiNG How-To Guide RSA SecurID_Overview
- WiNG version 4.0 Licensing_Configuration
- WiNG version 4.0 Licensing_Overview
- Hotspot Authentication - Configuration
- WiNG - Hotspot Authentication - Overview
- Motorola_Wireless IDS
- ARP Cache Poison detection
- Use of Adaptive AP for Limited WAN Bandwidth Deplo...
- Using OpenLDAP database with WS5100 on-board RADIU...
- How to encrypt my pass phrase in my config file
- Restore default password WS5100
- Configuring-Site-To-Site-VPN WS5100
-
▼
February
(36)
Labels
- 12222
- 12223
- 2710 Location Appliance
- 3G Wan
- 5246
- 5247
- 7920
- 7921
- 802.11
- 802.11a
- 802.11b
- 802.11e
- 802.11g
- 802.11i
- 802.11n
- 802.1p
- 802.3
- AC
- ACS 5.2
- AP
- AP Authentication
- AP fallback
- arp
- Autonomous
- autonomous AP
- AVVID
- background
- Beacon
- best effort
- best practices
- broadcast key
- CAC
- call admission control
- CAPWAP
- CCIE
- CCIE Wireless Female
- CCIE Wireless Leigh blog
- CCIE Wireless v2
- Cisco
- Cisco Live CCIE Routing and Switching Wireless CCNP Duplex rental property
- config advanced eap bcast-key-interval
- CWNA
- CWNP
- dhcp
- dhcp proxy
- Digital Certificates
- DSCP
- DTIM
- encrypt pass phrase
- etherchannel
- Fast Lane
- FastLane
- H-REAP
- Hotspot Authentication
- install ACS 5.2 laptop
- ip helper-address
- IPExpert
- Kara Muessig
- kilomicrosecond
- Kusec
- LAG
- LDAP
- license
- lightweight AP
- LWAPP
- LWAPP transport mode
- mappings
- Mesh Network
- Mesh Portfolio
- MFP
- millisecond
- mobility
- mobility security mode
- mobility tunneling mode
- Motorola
- ms
- MU to MU
- NAT
- onlinestudylist
- option 43
- option 60
- Pass
- QBSS
- QoS
- Radius & WPA
- Radius Attributtes
- RF
- RRM
- RSA SecurID
- Ruckus Wireless access points
- Secure
- session
- SMART-RF
- Snipe-IT
- static IP
- timeout
- traffic flow
- Ubuntu 11.10
- UP
- user idle
- video
- virtual IP
- VMWare Player 4.0.2
- voice
- voice control
- voice data rate
- vpn
- WAP
- WCS
- wired
- Wireless
- Wireless Filters
- Wireless IDS
- WLAN
- WLC
- WLC QoS profile
- WMM
- working with WCS
- WS5100
Recent Posts
Popular Posts
-
RADIUS Authentication Attributes: The RADIUS protocol follows client-server architecture and uses the User Datagram Protocol (UDP) as de...
-
Overview WiNG version 4.0 includes a rich suite of features which are included with each RF Switch at no additional charge as well as...
-
Snipe-IT is a free and open source, cross-platform, feature-rich IT asset management system built using a PHP framework called Laravel ...
-
Capturing 802.11 frames with Ruckus Wireless access points and Wireshark Since many problems can be resolved only by closely inspecti...
-
Components Used: The information in this document is based on the following Motorola hardware and software versions: 1 x RFS6000 or ...
-
WS5100 login: cli User Access Verification Username: restore Password: restoreDefaultPassword WARNING:This will wipe out the con...
-
Use of ARP Cache in a network device Most of the network devices will have anARP cache; the content of the same will be a collection of IP...
-
Requirements: The following requirements must be met prior to attempting this configuration: One RFS4000 or RFS6000 WLAN Switch Contr...
-
Components Used: The information in this document is based on the following hardware and software versions: · 1 x RFS4000 Swit...
-
The MU to MU disallow feature allows the RF Switch to block communications exchanged between clients associated to a WLAN.With the Motorola ...
Copyright (c) 2013 WIFITECHBLOG.











































0 nhận xét:
Post a Comment