Wireless Solutions, Best Solutions For You !
Ads 468x60px
Popular Posts
-
The MU to MU disallow feature allows the RF Switch to block communications exchanged between clients associated to a WLAN.With the Motorola ...
-
Pre-Requisites: Requirements: The following requirements must be met prior to attempting this configuration: One (or more) RF Switc...
-
RADIUS Authentication Attributes: The RADIUS protocol follows client-server architecture and uses the User Datagram Protocol (UDP) as de...
-
LDAP Server can be used as the database with WS5100 radius server. This document provides the details of configuration need to done for WS5...
-
WS5100 login: cli User Access Verification Username: restore Password: restoreDefaultPassword WARNING:This will wipe out the con...
-
IPSec VPN offers the security and encryption features necessary to protect enterprise data, voice, and video traffic as it traverses public...
-
Components Used: The information in this document is based on the following hardware and software versions: · 1 x RFS4000 Swit...
-
The following section outlines the configuration steps required to configure 802.11i with 802.1X and pre-shared keys on a RF Switch: 1) ...
-
Snipe-IT is a free and open source, cross-platform, feature-rich IT asset management system built using a PHP framework called Laravel ...
WiNG How-To Guide 3G WAN
Introduction:
3G or 3rd Generation is a family of standards for
mobile telecommunications defined by the International Telecommunication Union
which includes GSM, UMTS, CDMA as well as DECT and WiMAX. Compared with 2G or
2.5G, 3G offers simultaneous speech and data services and improved data rates
allowing network operators to offer a wider range of advanced services to subscribers
while achieving greater network capacity through improved spectral efficiency.
3G Applications:
3G WAN support is available on the RFS4000/RFS6000
WLAN Switch Controllers running WiNG 4.1.0.1 and above and can be deployed to
provide primary Internet access at a remote site or Internet failover in the event
of a primary wireline Internet service failure.
Primary Internet Access:
For primary Internet access the 3G WAN card provides
the primary outbound path for the site to the public Internet. Once connected
the 3G card interface will receives network addressing from the service providers
DHCP server and the WLAN Switch Controller will use the service provider’s
upstream router as its default route.
For primary Internet access a NAT rule must be
defined that translates internal private addresses to the Public IP address
assigned to the 3G interface. Note that unlike virtual IP interfaces, the 3G
interface is automatically designated as a NAT outside interface.
Internet Failover:
For Internet failover the 3G WAN card provides a
backup Internet path to a wireline Internet service directly connected to the
WLAN Switch Controller. During normal operation the WLAN Switch Controller will
use the wireline Internet service and all outbound Internet traffic will be
forwarded to the wireline service provider’s router. The wireline service
provider’s router is dynamically or statically defined as the WLAN Switch
Controller’s default router.
To detect a wireline Internet service failure the
WLAN Switch Controller monitors the state of the default router will failover
to the 3G interface if the default router becomes unreachable. Outbound
Internet will failover to the 3G interface if:
1) The
physical port that the default router is connected through goes down.
2) The
default router is no longer reachable by the WLAN Switch Controller.
If the wireline service provider’s router becomes
unreachable, the WLAN Switch Controller will dynamically update the NAT rule to
use the 3G interface as well as dynamically update the routing table so that
the 3G WAN service provider’s upstream router becomes the default gateway for
the WLAN Switch Controller. All outbound traffic destined to the public
Internet will then be forwarded via the 3G interface.
3G WAN Express Card Support:
3G WAN Express cards are available from a number of
service providers in each region and each card will require a data service plan
from a service provider. The available data service plans vary by region and
service provider and can ether permit unlimited data transfer or limited data
transfer over the service providers 3G network. Service provides may also apply
overage fees when a specific amount of traffic has been exceed.
The following table provides a list of supported 3G
WAN Express cards supported by the RFS4000/RFS6000 WLAN Switch Controllers
available by region and service provider. Before selecting a3G Express card it
is recommended that you reference the latest release notes for the latest list
of supported cards as new models are being continuously introduced into the
market.
3G Bandwidth:
The amount of throughput available over a 3G service
provider’s network will vary depending on the 3G technology and each service
provider’s implementation. The current generations of 3G access technologies
are fully capable of providing comparable throughput to wireline based Internet
services, however the radio technologies, backbone and Internet capacity core
will ultimately determine the actual amount of throughput that is available at
each branch site.
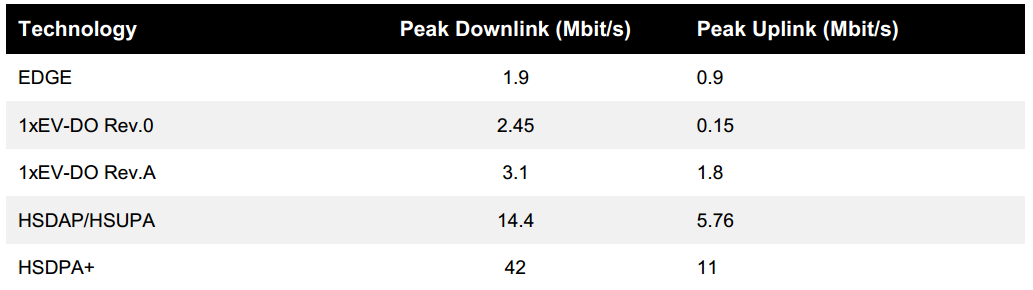
The following table lists the theoretical peak
uplink and downlink throughputs that are for each 3G wireless access
technology. The actual throughput and performance at a branch site will vary
based on the distance of the 3G card from the cellular base station, interference
and each service provider’s specific 3G implementation.
3G Performance:
3G WAN performance at a site will also be impacted
by number of physical factors including the antenna orientation, distance
between the antenna and cellular base station, physical obstructions and
external radio frequency (RF) interference.
The 3G Express card will be physically installed in
the RFS4000/RFS6000 WLAN Switch Controller and thus the coverage will vary at
the site depending on where the RFS4000/RFS6000 WLAN Switch Controller is physically
installed at the site.Prior to deployment it is strongly recommended that a
walkthrough of the site be performed with the 3G Express card installed in a
notebook PC to determine if adequate 3G signal strength is available where the
RFS4000/RFS6000 WLAN Switch Controller is to be installed. If the 3G signal is
low, the RFS4000/RFS6000 WLAN Switch Controller may need to be moved to an alternative
location where the 3G signal is improved.The following table provides a
coverage estimate based on signal strength in decibels per milliwatt (dBm).
Subscribe to:
Post Comments (Atom)
Recent Posts
Blog Archive
-
▼
2014
(36)
-
▼
February
(36)
- WiNG How-To Guide Wireless Filters - Configuration
- WiNG How-To Guide Wireless Filters - Overview
- WiNG How-To Guide 3G WAN - Configuration
- WiNG How-To Guide 3G WAN
- WiNG How-To Guide 802.11i - Configuration
- WiNG How-To Guide 802.11i - Overview
- WiNG How-To Guide Digital Certificates - Configura...
- WiNG How-To Guide Digital Certificates - Overview
- WiNG How-To Guide Microsoft L2TP/IPSec VPN Client-...
- WiNG How-To Guide Microsoft L2TP/IPSec VPN Client-...
- WiNG How-To Guide MU to MU Disallow
- Network Address Translation-Configuration
- Network Address Translation - Overview
- WiNG How-To Guide Secure Beacons - Configuration
- WiNG_ How To Secure_Beacons - Overview
- L3 Mobility Implementation With WS5100 version 3.0
- WiNG RADIUS Attributes
- SMART-RF – Overview
- Mesh Networking
- MWAN 6300 Series - MOTOMESH Solo
- Motorola Mesh Portfolio - Overview
- WS5100 3.0 Radius & WPA Implementatio - Configuration
- WS5100 3.0 Radius & WPA Implementatio - Overview
- WiNG How-To Guide RSA SecurID_Configuration
- WiNG How-To Guide RSA SecurID_Overview
- WiNG version 4.0 Licensing_Configuration
- WiNG version 4.0 Licensing_Overview
- Hotspot Authentication - Configuration
- WiNG - Hotspot Authentication - Overview
- Motorola_Wireless IDS
- ARP Cache Poison detection
- Use of Adaptive AP for Limited WAN Bandwidth Deplo...
- Using OpenLDAP database with WS5100 on-board RADIU...
- How to encrypt my pass phrase in my config file
- Restore default password WS5100
- Configuring-Site-To-Site-VPN WS5100
-
▼
February
(36)
Labels
- 12222
- 12223
- 2710 Location Appliance
- 3G Wan
- 5246
- 5247
- 7920
- 7921
- 802.11
- 802.11a
- 802.11b
- 802.11e
- 802.11g
- 802.11i
- 802.11n
- 802.1p
- 802.3
- AC
- ACS 5.2
- AP
- AP Authentication
- AP fallback
- arp
- Autonomous
- autonomous AP
- AVVID
- background
- Beacon
- best effort
- best practices
- broadcast key
- CAC
- call admission control
- CAPWAP
- CCIE
- CCIE Wireless Female
- CCIE Wireless Leigh blog
- CCIE Wireless v2
- Cisco
- Cisco Live CCIE Routing and Switching Wireless CCNP Duplex rental property
- config advanced eap bcast-key-interval
- CWNA
- CWNP
- dhcp
- dhcp proxy
- Digital Certificates
- DSCP
- DTIM
- encrypt pass phrase
- etherchannel
- Fast Lane
- FastLane
- H-REAP
- Hotspot Authentication
- install ACS 5.2 laptop
- ip helper-address
- IPExpert
- Kara Muessig
- kilomicrosecond
- Kusec
- LAG
- LDAP
- license
- lightweight AP
- LWAPP
- LWAPP transport mode
- mappings
- Mesh Network
- Mesh Portfolio
- MFP
- millisecond
- mobility
- mobility security mode
- mobility tunneling mode
- Motorola
- ms
- MU to MU
- NAT
- onlinestudylist
- option 43
- option 60
- Pass
- QBSS
- QoS
- Radius & WPA
- Radius Attributtes
- RF
- RRM
- RSA SecurID
- Ruckus Wireless access points
- Secure
- session
- SMART-RF
- Snipe-IT
- static IP
- timeout
- traffic flow
- Ubuntu 11.10
- UP
- user idle
- video
- virtual IP
- VMWare Player 4.0.2
- voice
- voice control
- voice data rate
- vpn
- WAP
- WCS
- wired
- Wireless
- Wireless Filters
- Wireless IDS
- WLAN
- WLC
- WLC QoS profile
- WMM
- working with WCS
- WS5100
Recent Posts
Popular Posts
-
RADIUS Authentication Attributes: The RADIUS protocol follows client-server architecture and uses the User Datagram Protocol (UDP) as de...
-
Snipe-IT is a free and open source, cross-platform, feature-rich IT asset management system built using a PHP framework called Laravel ...
-
Capturing 802.11 frames with Ruckus Wireless access points and Wireshark Since many problems can be resolved only by closely inspecti...
-
WS5100 login: cli User Access Verification Username: restore Password: restoreDefaultPassword WARNING:This will wipe out the con...
-
Use of ARP Cache in a network device Most of the network devices will have anARP cache; the content of the same will be a collection of IP...
-
Overview WiNG version 4.0 includes a rich suite of features which are included with each RF Switch at no additional charge as well as...
-
Components Used: The information in this document is based on the following Motorola hardware and software versions: 1 x RFS6000 or ...
-
Requirements: The following requirements must be met prior to attempting this configuration: One RFS4000 or RFS6000 WLAN Switch Contr...
-
Components Used: The information in this document is based on the following hardware and software versions: · 1 x RFS4000 Swit...
-
The MU to MU disallow feature allows the RF Switch to block communications exchanged between clients associated to a WLAN.With the Motorola ...
Copyright (c) 2013 WIFITECHBLOG.





























0 nhận xét:
Post a Comment